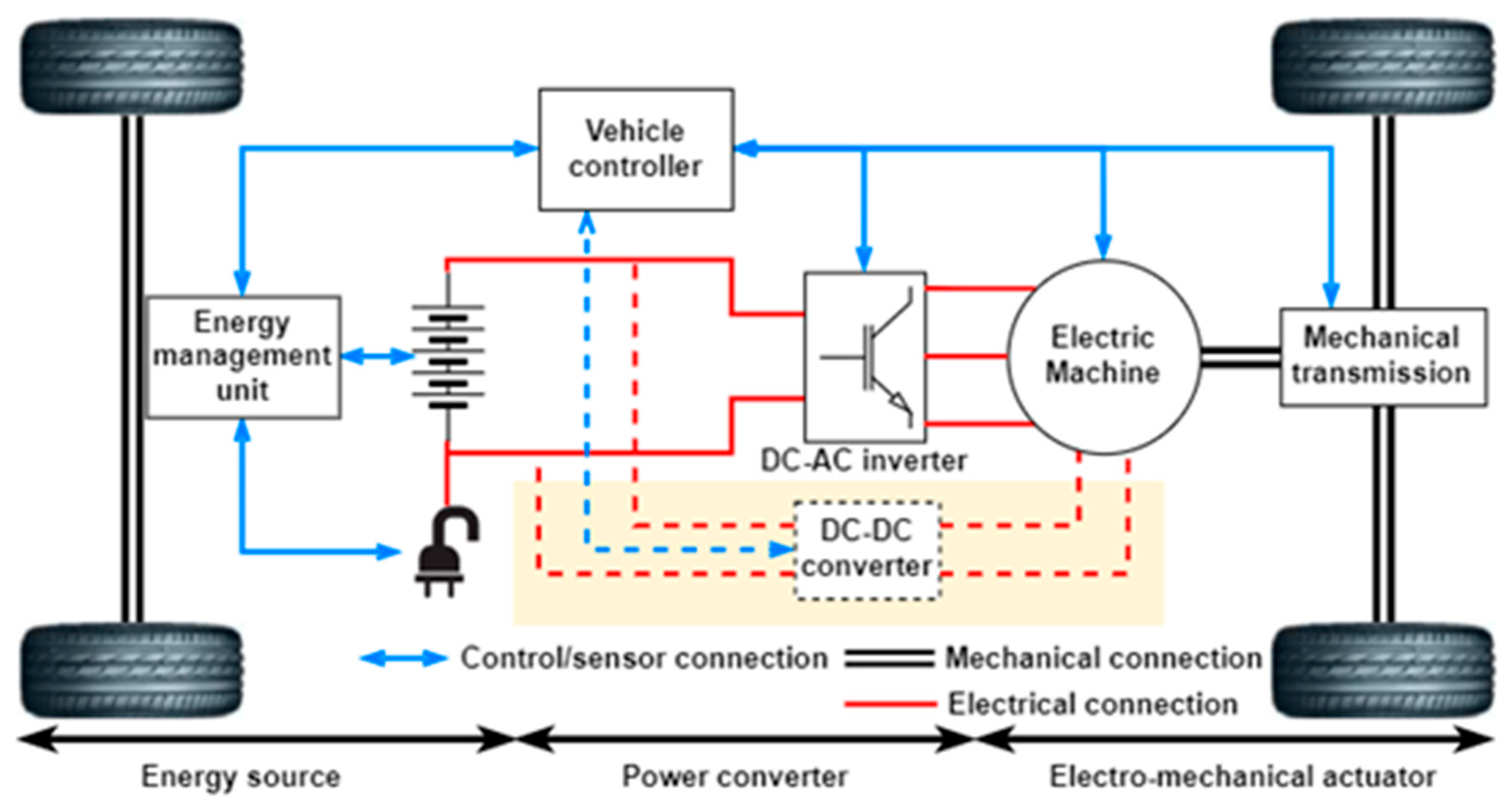
EV Architecture is complex and are comprises of Battery,Motor,PDU,MCU,Sensors,Harness,Controls and Aux Systems.
There are 2 types of major architecture in EV Vehicles.
1. 400V EV Architecture which are already available and got matured already.
2. 800V EV Architecture. which are taking control in Luxury space and automotive OEM's now switching focus on this architecture, why? will cover below.
There are advantages and disadvantage in both architecture, will see in details below.
1. 400V EV System Architecture
The 400V architecture is the standard EV architecture which uses Voltage range from 300V to 500V and it is also cheaper to implement, the main reason is that most OEMs have already established suppliers of components and the supply chain is very strong unlike 800V Systems.
The Production cost of 400V Systems are cheaper to manufacture than 800V systems and finally the end users can reap benifit from this cost reduction in the over all purchase price of the EV vehicle.
Thats the reason the 400V Architecture ev vehicles tends to sell more and placed in the mid and cheaper catogory.
TATA Nexon Max
Lithium ion battery Voltage - 332.8V
Capacity - 120AH
Power - 39.9KW
The TATA Nexon EV Car uses 400V architecture.
2. 800V EV System Architecture
The 800V architecture are usually found in the Luxuary segments of EV vehicles where the arrangements of the components and systems are neater and less clumsey.
There are lot more advantages in 800V system than the 400V systems, simply put the voltages of a system increases then the current needed decreases to get the same amount of power.
Eg:
Case 1: 400V,200A = 80000W or 80KW
Case 2: 800V,100A = 80000W or 80KW
Take Case 1, Since it uses 400V architecture the max current it can withdraw is around 1C that is 200A to achieve 80KW of power to the load(Motor).
Click to know about C -Rate?
Take Case 2, The 800V architecture uses only 100A to draw maximum power output of 80KW.
Advantages of 400V Architecture:
1. Widespread Infrastructure availability of charging stations upto 150KW Fast chargers and increasing.
2. Lower costs of Subsystems & Components.
3. Overall vehicle purchase cost is low.
4. Matured industry from production to supply chain availablity.
5. Reliable and proven technology.
Disadvantages of 400V Architecture:
1. Limited power output levels due to lower system voltages cap at 400V.
2. Doesnt support Ultra Fast Charging, Limited fast charging capability capped to its system voltage.
3. Increased resistive losses at higher power output.
Advantages of 800V Architecture:
1. Supports Ultra Fast Charging upto 350KW due to its high voltage and lower current requirements.
2. Resistive power losses are low compared to 400V systems since the current needed is less and losses will be low.
3. The sizes of HVcomponents and the cables will be lighter since it uses high voltage and lower current than 400V systems.
4. Higher efficiency and Performance.
5. Overall reduction in Weight of the vehicle.
6. Future proof since the coming years OEM's increasing their focus on 800V architecture.
Disadvantages of 800V Architecture:
1. Few Ultra Fast Charging stations, Infrastucture is not widespread compared to 400V architecture ev vehicles.
2. Higher costs of Components.
3. The overall vehicle costs are higher.












_front_view.png)