 |
| Image 1: AI Generated EV vehicle electric motor |
Fundamental Physics:
1. Force: A Push or Pull experinced by any object is called a force.
2. Current: Movement of electrons in a conductors causes current to flow from higher potential to lower Potential ( Like Water as a current moves from Tank to a small Tap).
3. Electron: Electron is a fundamental subatomic particle and , it is also known as an elementary particle because it can't be break into any other sub particle.
Electron flows from Negative of the power source to the Positive, Since electron have -ve Charge and only electron moves in an atom unlike Proton & Neutron so the movement of electron will be from Negative to Positive in a source like Battery.
4. Magnetic Field: It is an invisible Force (Lorentz Force) that an Object or Charge carriers (Electrons,Holes,Ions) experinces around a magnetic material like Magnets.
5. Fleming's Left Hand Rule:
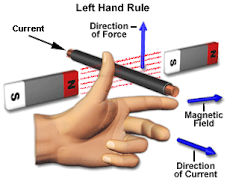 |
| Image 2: Fleming's Left Hand Rule , Rajiv1840478, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons |
As shown in the above image,The Fleming's left hand rule is applicable only for Motors, Which says whenever an conductor placed in a magnetic field the conductor experinces a Force (F) which will be perpendicular to the dirction of Magnetic Field (B) and the Current (I).
6. Fleming's Right Hand Rule:
 |
| Image 3: Fleming's Right Hand Rule , Douglas Morrison DougM, CC BY-SA 3.0 |
As shown in the above image (2),The Fleming's right hand rule is applicable for Generators, Which says whenever an conductor is moved in a magnetic field an emf will be induced across the conductor and if the conductor is in a closed path or loop then the induced emf will cause a current to flow.
The Direction of movement of Conductor (F) which will be perpendicular to the dirction of Magnetic Field (B) and the Current (I).
DC Motor:
 |
| Image 4: Rotation of Rotor inside an Electric Motor |
A Motor is a device which converts input electrical energy to output mechanical energy.
Components of a Simple DC Motor:
A Motor consists of major components which are,
1. Stator (D) - It is a static segment of a motor in which magnetic fields are created by Permanent Magnet or Electromagnet.
2.Rotor/Armature (C) - It is a rotating segment of a motor which is made up of steel,copper coils and a shaft.
3.Commutator (A) - It is a segment of the rotor in which the terminals of the rotor winding is conneted which periodically revereses the direction of the supplied current through brushes.
4.Brushes (B) - It is used to transfer power from the fixed electrical contact or wire to the rotating commutator.
Working of a Electric Motor:
The above image is a simple model that explains the working of an electric motor.
The Magnets magnetic fields always travel from Northpole to Southpole outside magnets and from S to N inside the magnets.
The Magnetic field lines are drawn from N ----> S that is denoted as letter (B) in the above image.
Direction of Force exerted is denoted by letter (F) & Current as (I).
As per Feradays Left hand Rule which is applicable only to Motors, When we supply power to the armature carrying coils, a magnetic field will be generated and interacts with the stators magnetic field since the opposite poles of the magnets attracts each other the rotor starts to rotate a half.
But there is an issue still not seen , The Motor can't rotate another half because the magnetic field of rotor and stator is in parellel and alligned now.
The solution is to either flip the magnets or to flip the power source like battery for every half cycle but the easier and the effective method to resolve this problem is to introduce a segment called Commutator.
The commutator is a circular split type ring and its job is to flip the polarity of current supplied through the brushs. The brush is a fixed contact or a metal piece which will be in contact with the commutator always.
The Commutator rotates with the armature or rotor but the power supplying brushes are in fixed position so that the polarity of current is fliped for every half rotation.
This resolves the issue and the motor will rotate contineously.
The torque of the motor can be varied by either improving the strength of the magnetic field by increasing the cross section of the coil or by increasing the number of turns of the coil or by increasing the current flowing through the coil.







No comments:
Post a Comment